Cryogenic Freezer can reduce post-harvest losses of Bangladesh
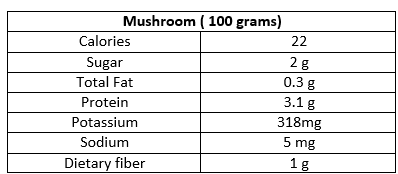
Proper post-harvest handling and storage of food produces are equally important to the intensive and extensive farming in securing food for a nation. A survey revealed that post-harvest losses of Fruits and Vegetables at 23.6 to 43.5 percent of the total production in Bangladesh. This loss can be »