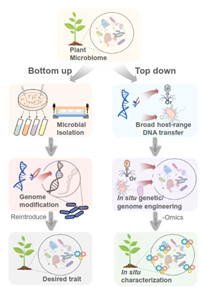
Plant microbiome engineering is the process of manipulating the microbial communities that live in and around plants to improve their growth, health, and productivity. The plant microbiome consists of a complex community of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that interact with the plant host in various ways, such as providing nutrients, protecting against pathogens, and regulating plant growth and development. One approach to plant microbiome engineering is to use probiotics or biofertilizers, which are formulations of beneficial microbes that can be applied to the soil or plant surfaces to enhance plant growth and health. Another approach is to use genetic engineering to introduce genes into the plant microbiome that encode traits such as disease resistance, nutrient utilization, or stress tolerance. Recent advances in DNA sequencing and computational analysis have provided new tools for studying the plant microbiome and identifying key microbial species that contribute to plant health and productivity. This knowledge can be used to design more effective microbiome engineering strategies that target specific microbial species or metabolic pathways. Plant microbiome engineering has the potential to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability by reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, while also enhancing the nutritional content of crops. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complex interactions between plants and their microbiomes and to develop safe and effective microbiome engineering approaches. There are two approaches for the genetic/genome engineering of plant microbiomes. The bottom-up approach isolates plant-associated microbes and modifies individual strains for desired traits, then inoculates plants with the modified strains. The top-down approach uses horizontal gene transfer to introduce traits into a broad range of hosts in situ and then determines their phenotypes by using supporting devices and omic technologies (Trends in Biotechnology, 2021).
Dr. Md. Monirul Islam
Senior Scientists
ASRBC, ACI Seed